De novo OTU picking from long amplicons with LACA
LACA is a reproducible and scalable workflow for Long Amplicon Consensus Analysis, e.g., 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis. It uses snakemake to manage the workflow and conda to manage the environment.
LACA installation
The full installation guide of LACA is available here.
You can choose to install LACA with docker image (which is only solution for MacOS users) or from the GitHub repository according to your OS and preference.
Docker image
The easiest way to use LACA is to pull the docker image from Docker Hub for cross-platform support.
docker pull yanhui09/laca
LACAis built forlinux/amd64platform, with cross-platform support throughdocker.
MacOSusers needs to use docker container to runLACA.
Installation from GitHub repository
1. Clone the Github repository and create an isolated conda environment
git clone https://github.com/yanhui09/laca.git
cd laca
mamba env create -n laca -f env.yaml
2. Install LACA with pip
To avoid inconsistency, we suggest installing LACA in the above conda environment
conda activate laca
pip install --editable .
A demo run with LACA
Find a full usage guide here.
Example with a quick start
laca init -b /path/to/basecalled_fastqs -d /path/to/database # init config file and check
laca run all # start analysis
Get familiar with LACA usage
LACA is easy to use. You can start a new analysis in two steps using laca init and laca run .
Remember to activate the conda environment if LACA is installed in a conda environment.
conda activate laca
laca -h
To use the docker image, you need to mount your data directory, e.g., pwd, to the /home in the container.
docker run -it -v `pwd`:/home --privileged yanhui09/laca
laca -h
1. Intialize a config file with laca init
laca init will generate a config file in the working directory, which contains the necessary parameters to run LACA.
laca init -h
2. Start analysis with laca run
laca run will trigger the full workflow or a specfic module under defined resource accordingly. Get a dry-run overview with -n. Snakemake arguments can be appened to laca run as well.
laca run -h
Run LACA with a demo dataset
0. Make sure you have downlowded the required demo dataset from here. And the enter the directory with cd.
E.g., Enter a directory with an absolute path (“long path”) is /home/me/MAC2023-extra.
cd /home/me/MAC2023-extra
If you haven’t downloaded the data yet and with Git installed,
git clone https://github.com/yanhui09/MAC2023-extra.git
cd ./MAC2023-extra
1. Check where you are and try laca init, check the genereated config.yaml file.
pwd
laca init -b ./data/ont16s -d ./database -w ./laca_output --fqs-min 50
cat ./laca_output/config.yaml
2. Start LACA in a dry and real run
laca run all -w ./laca_output -n
laca run kmerCon -j 4 -w ./laca_output
LACA is able to generate otu table, taxonomy table and phylogenetic tree if you run the full workflow with laca run all. But it takes time to prepare the database and installation for the first use.
As an example, here we only run the kmerCon module to extract consensus sequences based on kmer frequency.
Take a look at these consensus sequences, take the first one for BLAST search against rRNA/ITS database.
head -n2 ./laca_output/kmerCon/kmerCon.fna
Expected output:
>pooled_0b000_0cand1
CACAATGGGCGCAAGCCTGATGCAGCGACGCCGCGTGCGGGATGACGGCCTTCGGGTTGTAAACCGCTTTTGACTGGGAGCAAGCCCTTCGGGGTGAGTGTACCTTTCGAATAAGCACCGGCTAACTACGTGCCAGCAGCCGCGGTAATACGTAGGGTGCAAGCGTTATCCGGAATTATTGGGCGTAAAGGGCTCGTAGGCGGTTCGTCGCGTCCGGTGTGAAAGTCCATCGCTTAACGGTGGATCCGCGCCGGGTACGGGCGGGCTTGAGTGCGGTAGGGGAGACTGGAATTCCCGGTGTAACGGTGGAATGTGTAGATATCGGGAAGAACACCAATGGCGAAGGCAGGTCTCTGGGCCGTCACTGACGCTGAGGAGCGAAAGCGTGGGGAGCGAACAGGATTAGATACCCTGGTAGTCCACGCCGTAAACGGTGGATGCTGGATGTGGGGACCATTCCACGGTCTCCGTGTCGGAGCCAACGCGTTAAGCATCCCGCCTGGGGAGTACGGCCGCAAGGCTAAAACTCAAAGAAATTGACGGGGGCCCGCACAAGCGGCGGAGCATGCGGATTAATTCGATGCAACGCGAAGAACCTTACCTGGGCTTGACATGTTCCCGACAGCCGTAGAGATACGGCCTCCCTTCGGGGCGGGTTCACAGGTGGTGCATGGTCGTCGTCAGCTCGTGTCGTGAGATGTTGGGTTAAGTCCCGCAACGAGCGCAACCCTCGCCCTGTGTTGCCAGCACGTCGTGGTGGGAACTCACGGGGGACCGCCGGGGTCAACTCGGAGGAAGGTGGGGATGACGTCAGATCATCATGCCCCTTACGTCCAGGGCTTCACGCATGCTACAATGGCCGGTACAACGGGATGCGACCTCGCGAGGGGGAGCGGATCCCTTAAAACCGGTCTCAGTTCGGATTGGAGTCTGCAACCCGACTCCATGAAGGCGGAGTCGCTAGTAATCGCGGATCAGCAACGCCGCGGTGAATGCGTTCCCGGGCC
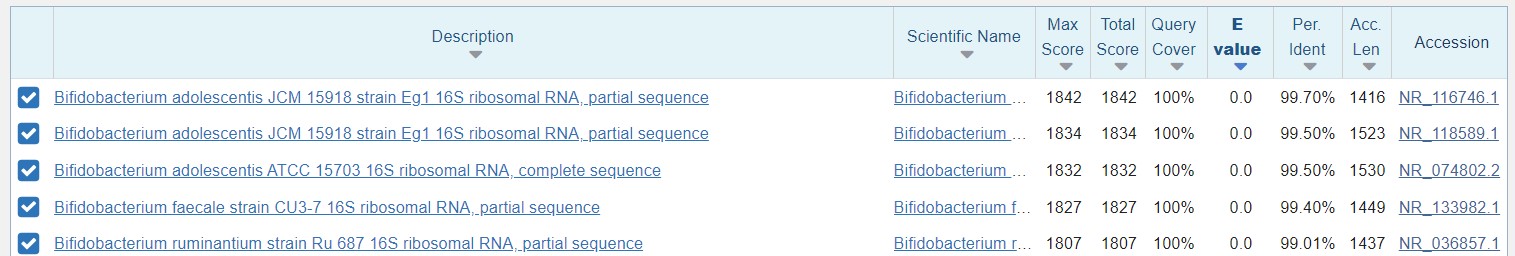
The BLAST result indicates that this sequence is a 16S rRNA gene fragment from Bifidobacterium with over 99% identity.
Take one ONT read and do the same
BLASTsearch. What do you expect to see?zcat ./data/ont16s/*.fastq.gz | head